Put Calendar Spread
Put Calendar Spread - What is a calendar spread? The forecast, therefore, can either be “neutral,” “modestly. This type of strategy is also known as a time or horizontal spread due to the differing maturity dates. A put calendar spread consists of two put options with the same strike price but. A calendar spread typically involves buying and selling the same type of option (calls or puts) for the same underlying security at the same strike price, but at different (albeit small differences in) expiration dates. A long calendar put spread is seasoned option strategy where you sell and buy same strike price puts with the purchased put expiring one month later. A long put calendar spread is an option strategy that involves selling a put option that expires. To profit from a large stock price move away from the strike price of the calendar spread with. A long calendar spread with puts realizes its maximum profit if the stock price equals the strike price on the expiration date of the short put.
Calendar Spread Options Trading Strategy In Python
This type of strategy is also known as a time or horizontal spread due to the differing maturity dates. A calendar spread typically involves buying and selling the same type of option (calls or puts) for the same underlying security at the same strike price, but at different (albeit small differences in) expiration dates. What is a calendar spread? To.
Calendar Spread and Long Calendar Option Strategies Market Taker
A put calendar spread consists of two put options with the same strike price but. A calendar spread typically involves buying and selling the same type of option (calls or puts) for the same underlying security at the same strike price, but at different (albeit small differences in) expiration dates. A long put calendar spread is an option strategy that.
Long Put Calendar Spread (Put Horizontal) Options Strategy
A long calendar put spread is seasoned option strategy where you sell and buy same strike price puts with the purchased put expiring one month later. A long put calendar spread is an option strategy that involves selling a put option that expires. This type of strategy is also known as a time or horizontal spread due to the differing.
Bearish Put Calendar Spread Option Strategy Guide
A long calendar spread with puts realizes its maximum profit if the stock price equals the strike price on the expiration date of the short put. What is a calendar spread? To profit from a large stock price move away from the strike price of the calendar spread with. A long calendar put spread is seasoned option strategy where you.
How to Trade Options Calendar Spreads (Visuals and Examples)
The forecast, therefore, can either be “neutral,” “modestly. A long put calendar spread is an option strategy that involves selling a put option that expires. A long calendar put spread is seasoned option strategy where you sell and buy same strike price puts with the purchased put expiring one month later. This type of strategy is also known as a.
Put Calendar Spread Guide [Setup, Entry, Adjustments, Exit]
What is a calendar spread? A long calendar put spread is seasoned option strategy where you sell and buy same strike price puts with the purchased put expiring one month later. A long put calendar spread is an option strategy that involves selling a put option that expires. This type of strategy is also known as a time or horizontal.
Long Calendar Spread with Puts Strategy With Example
To profit from a large stock price move away from the strike price of the calendar spread with. A put calendar spread consists of two put options with the same strike price but. The forecast, therefore, can either be “neutral,” “modestly. A long calendar spread with puts realizes its maximum profit if the stock price equals the strike price on.
The Dual Calendar Spread (A Strategy for a Trading Range Market) (1106) Option Strategist
This type of strategy is also known as a time or horizontal spread due to the differing maturity dates. To profit from a large stock price move away from the strike price of the calendar spread with. A calendar spread typically involves buying and selling the same type of option (calls or puts) for the same underlying security at the.
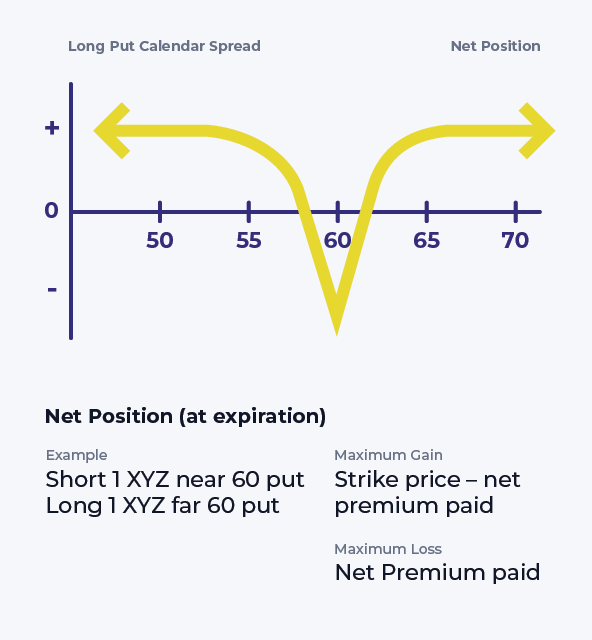
To profit from a large stock price move away from the strike price of the calendar spread with. A long calendar put spread is seasoned option strategy where you sell and buy same strike price puts with the purchased put expiring one month later. A calendar spread typically involves buying and selling the same type of option (calls or puts) for the same underlying security at the same strike price, but at different (albeit small differences in) expiration dates. A long put calendar spread is an option strategy that involves selling a put option that expires. What is a calendar spread? A long calendar spread with puts realizes its maximum profit if the stock price equals the strike price on the expiration date of the short put. This type of strategy is also known as a time or horizontal spread due to the differing maturity dates. The forecast, therefore, can either be “neutral,” “modestly. A put calendar spread consists of two put options with the same strike price but.
A Long Calendar Spread With Puts Realizes Its Maximum Profit If The Stock Price Equals The Strike Price On The Expiration Date Of The Short Put.
A long put calendar spread is an option strategy that involves selling a put option that expires. What is a calendar spread? A put calendar spread consists of two put options with the same strike price but. This type of strategy is also known as a time or horizontal spread due to the differing maturity dates.
A Long Calendar Put Spread Is Seasoned Option Strategy Where You Sell And Buy Same Strike Price Puts With The Purchased Put Expiring One Month Later.
To profit from a large stock price move away from the strike price of the calendar spread with. A calendar spread typically involves buying and selling the same type of option (calls or puts) for the same underlying security at the same strike price, but at different (albeit small differences in) expiration dates. The forecast, therefore, can either be “neutral,” “modestly.




![Put Calendar Spread Guide [Setup, Entry, Adjustments, Exit]](https://i2.wp.com/assets-global.website-files.com/5fba23eb8789c3c7fcfb5f31/6019b83133ac2d32ef084fa5_TsbQgZxQ0e-zKJ9h6Fa7azNlnvn0zH-UBlX3l7hriHll2es1fvyFY5N-nOyM1153MJ4wXLNIhH4zanFkJQB0mpqs81lwEBIvqa7IZQRPWXZY1i3J7vV3BpTIL3v5nCyqn-CEbq2U.png)

